GD & T: FITS
· It is the degree of tightness or looseness between two mating parts or components.
· There are three different types of Fits mentioned below uses in GD & T.
CLEARANCE FIT
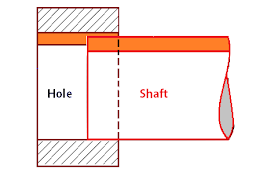
· Clearance fit is one in which two assembled parts can move freely without any distraction in its assembled condition.
· In clearance fit system upper limit of shaft is less than the lower limit of hole.
· It is the difference between the size of the hole and size of the shaft or pin is known as clearance.
· Clearance always provides positive allowance.
· The parts comes under the clearance fit can be assembled by hand or manually.
· Examples: Door hinge, wheel and axle, shaft and bearing, shaft and bush etc.
· Clearance fit is classified into loose fit, Running fit & Slide fit or Medium fit.
· In loose fit mating parts does not required precise dimensions, it used in basic pulleys, lifting lug and its pin and other agricultural equipment’s.
· In running fit the dimensional tolerances are kept in such a way that a small film of oil is available into two mating parts like cylinder and piston arrangement.
· Slide fit provides medium tolerance in such a way that the both mating parts can easily slide over each other.
INTERFERENCE FIT
· It defines that assembly of two mating parts having male part dimension is quite higher than the female part dimension that means upper limit of shaft size is higher than the lower limit of hole size.
· Interference fit is given for the assembly of parts to obtain a rigidity and restrict the relative motion between two mating parts.
· Examples. Bearing into casting, dowel pin etc.
· The difference between size of shaft and size of hole is called interference.
· Interference fit is classified into shrink fit, force fit and press fit.
· In shrink fit one of the component is heated and then assemble. This assembly is cooled up to normal temperature.
· It uses the thermal expansion technique.
· Example: Railway wheels, rim fitment into iron tyre etc.
· In force fit the pressure or force is controlled by the assembly.
· The moderate pressure is required to assemble the mating parts.
· Example: Car wheels, Armature of Dynamo etc.
· In press fit assembly of two mating parts or components can be done by hand with the help of hammer or using light pressure.
· Example: Key-pulley and shaft, Rockers arm etc.
TRANSITION FIT
· In transition fit the upper limit of shaft diameter is higher than the lower limit of hole diameter.
· It is neither too loose like clearance fit nor too tight like interference fit, it is the intermediate stage between above two fits.
· It is having three types that are Push fit, force fit and wringing fit.
· In push fit very light pressure is applied on one of the mating part in the assembly.
· The assembly having least vibration during working.
· It is also known as snug fit. Example: Pin and hole.
· Force fit is the assembly of two mating parts in such a way that the one part could not move separately after assembly.
· Hole may be expanded by heating if required during assembly. Example: Railway wheels.
· In Wringing fit slight negative allowance exist between two mating parts in the assembly.
· It is used in fixing of keys, pins etc.


Comments
Post a Comment